We have all, at least, come across this question or have silently asked ourselves and most probably ended up with a murmured answer.
Well, today we are going to answer the question and settle our doubts once and, hopefully, for all.
Defining a variable
A variable is a container meant to hold a value to be used later. A more dictionary kinda definion reads like: A variable is a named memory location whose contents may change in the course of the program execution. 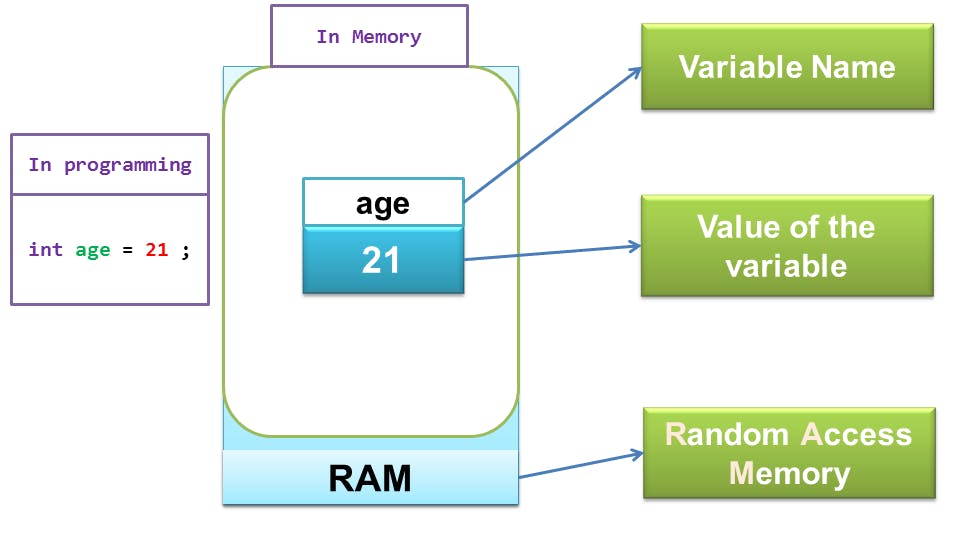 It is important to note that the contents of this contaner (the value) might change later on. I like to think of variables like a hotel room that one can book and later go in and spend a night or so. You can be given any room and the room you have been assigned to should not be given to anyone else unless you don't want it anymore (your vacation is over). In this room, you can also make a few changes as you see fit. For instance, you can dim the lights a bit. As long as the room has not been assigned to anyone, the occupant is undefined.
It is important to note that the contents of this contaner (the value) might change later on. I like to think of variables like a hotel room that one can book and later go in and spend a night or so. You can be given any room and the room you have been assigned to should not be given to anyone else unless you don't want it anymore (your vacation is over). In this room, you can also make a few changes as you see fit. For instance, you can dim the lights a bit. As long as the room has not been assigned to anyone, the occupant is undefined.
Variables in JavaScript
In JavaScript, just like any other scripting or programming language, we can declare, assign(initialize) and use variables in our programs.
Declaring Variables in JavaScript
There are three keywords to master when it comes to declaring variables in js:
varlet
With var we can declare our variable as follows:
// Declare a variable using var keyword
var car;
With let our declaration will look like:
// Declare a variable using let keyword
let car;
If you are new to this, by now you must be like "Ah! What is the difference?" Don't worry, I got you.
Assigning Variables in JavaScript
It will be useless, a waste of memory resources and, of course, typing energy to just declare variables without storing something in there. Remember we said they are like hotel rooms, uh? Let us assign some values to these containers then.
We had already declared the variables. Let us now assign the values.There are two ways in which we can initialize variables.
Declaring and assigning in different statements
// Declare a variable using var keyword
var car ;
// assigning a value
car = "myNewCar";
With let our declaration will look like:
// Declare a variable using let keyword
let car;
// assigning a value
car = "myNewCar";
Declaring and assigning in one statement
// Declare a variable using var keyword and assigning a value
var car = "myNewCar";
With let our declaration will look like:
// Declare a variable using let keyword and assigning a value
let car = "myNewCar";
Using Variables in JavaScript
In whichever method you declared and assigned your variables, they are ready now to be consumed by you program. For instance we can print the variable to the console log as shown below:
// Print our variable
console.log(car);
// output: myNewCar
Note that JavaScript assigns undefined to an unitialized variable.
// declare a variable test
let test;
// try to use/access test before initializing
console.log(test);
//output: undefined
This is because their is no value in the container just like when you try to reach out to someone in a room without an occupant.
Key Takeaways
A variable is a named memory location whose contents can during the program execution
In Javascript, keywords used to declare variables are:
varandletA variable can be initialized or assigned a value as follows:
let car = "myNewCar"Uninitialized variables are assigned a value of
undefined
In this blog, we have looked at what variable is, how to declare one and use it in JavaScript. As you might have noticed, we used only one variable "myNewCar" and you might be wondering what else you can store in JS variables. Well, there are many types of variables.